Application Security (AppSec) is now a must. Web apps, APIs, and cloud systems are attractive targets for hackers. They may steal data from the software. Moreover, the attacked app can even disrupt operations and end up harming reputations. Without strong app security, your business will suffer from costly fines and downtime. Finally, you will lose customer trust.
This guide explains what application security means and why you need it. You can also explore modern defense methods like SAST, DAST, and IAST. We have proven practices to secure apps, APIs, and cloud-native environments. So, keep reading to discover!
What is Application Security?
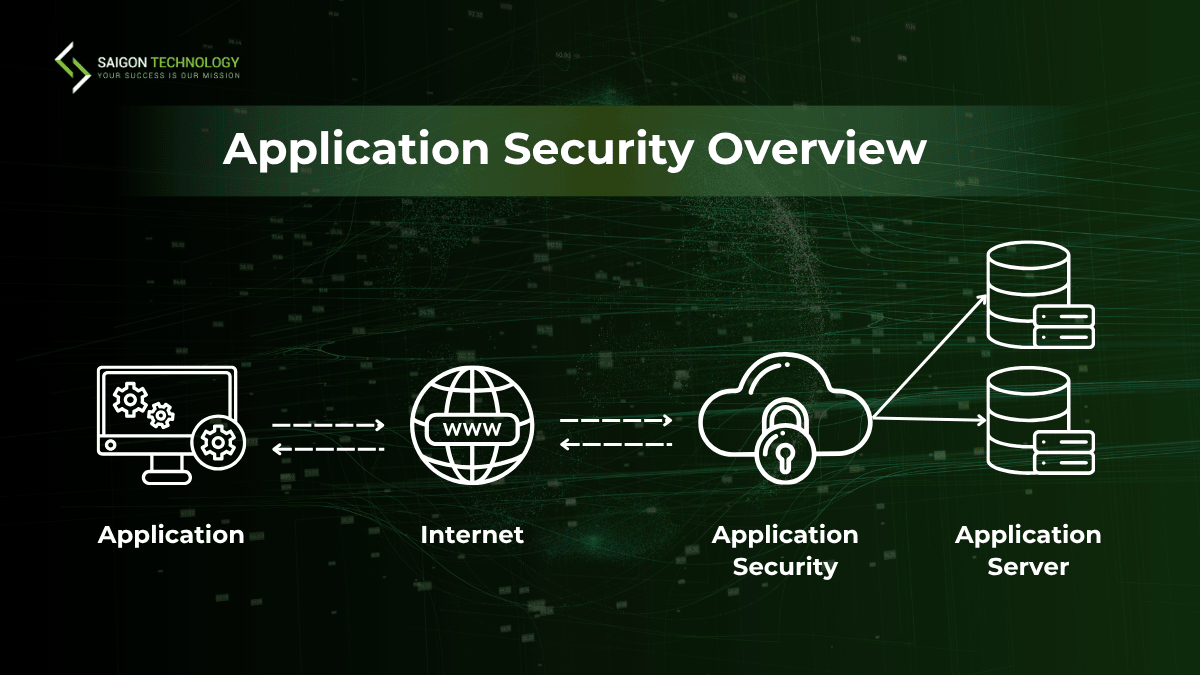
Application Security (AppSec) is the process of protecting software applications from threats, vulnerabilities, and unauthorized access throughout their lifecycle. This task covers design, development, testing, deployment, and maintenance.
Strong protection measures help protect data and ensure complete system security. The methods include secure coding practices and robust access controls. You will work on encryption and data protection, too. Authentication and authorization demand the same attention.
Businesses strengthen defenses through various techniques. Threat modeling and vulnerability scanning are among the most popular. Other application security testing methods are penetration testing, logging, and monitoring. There are many frameworks to try, such as OWASP Top Ten and NIST SP. Businesses can then secure data, apps, and users against cyber risks.
Why Application Security Matters?
This practice protects apps and sensitive data from cyber threats. Strong application security protection ensures application data security. Businesses can maintain their continuity. Moreover, a secure app means they follow industry regulations and avoid costly breaches. If you fail to apply it, you will encounter data theft and reputational damage. Expect legal consequences and significant remediation costs, too. Here’s what it matters:
- Protecting sensitive data: Apps often have personal details, financial records, and intellectual property. Thus, you need strong AppSec to keep it safe. Strong AppSec will help prevent leaks, breaches, and unauthorized access.
- Preventing costly branches: IBM’s Cost of a Data Breach Report 2024 said that a breach might cost USD 4.88 million. The positive news is that proactive defenses can lower the risk of financial damage.
- Business continuity: Cyberattacks like ransomware and downtime disrupt operations. AppSec addresses application security challenges early. Thus, businesses can maintain their continuity.
- Compliance with regulations: Fields like healthcare, finance, or e-commerce have many rules. AppSec comes to the rescue as it ensures compliance.
- Customer trust and brand image: Customers always prefer companies with a strong security posture. Yet, breaches or any security issues can damage your reputation.
- Lower long-term costs: Testing while development saves money by fixing errors early. Otherwise, you have to spend more time fixing issues after release or a breach.
In short, application security testing matters because it keeps your confidential data safe. Risk assessment also ensures your app complies with industry standards. Moreover, with proper testing, you can maintain business operations and build customer trust.
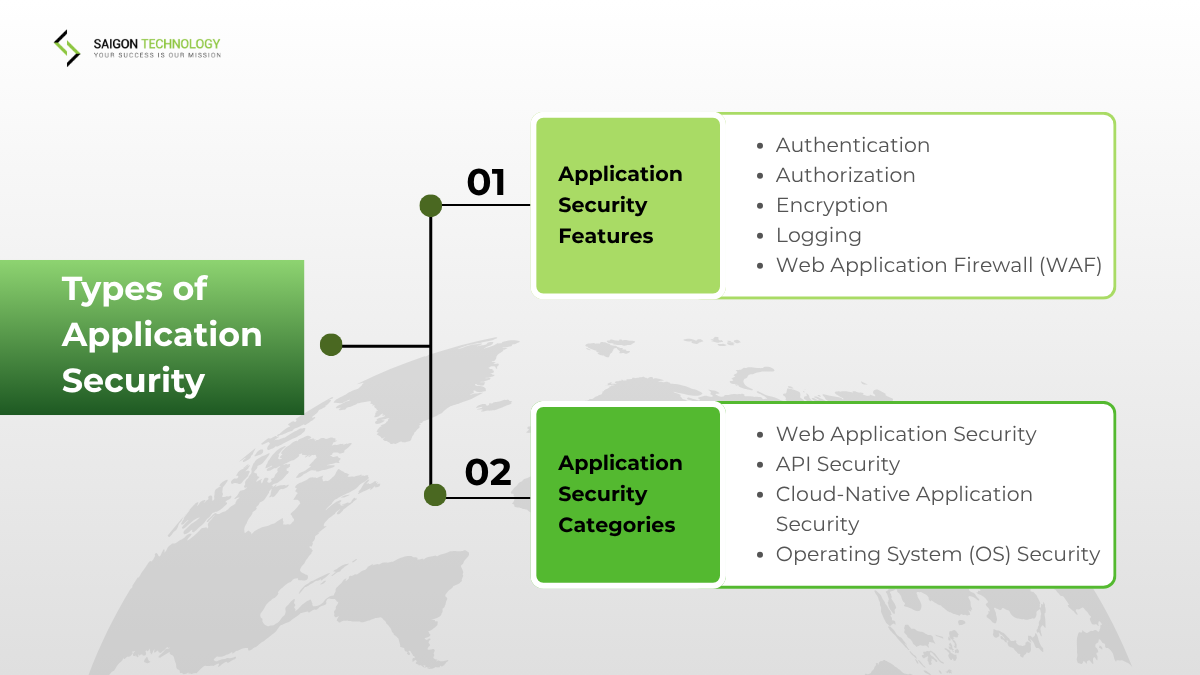
Types of Application Security
There are several ways to ensure you give your app comprehensive protection.
Application Security Features
The different types of application security features help protect software against threats. Authentication verifies user identity, while authorization controls access. Encryption keeps data safe. Logging tracks user activity. You can also use security testing to find vulnerabilities before hackers attack them.
Authentication
One of the app security features is about authentication. Application security testing strengthens identity verification. Users only receive access to the app when verified. This feature comes with access control policies.
Example: Passwords, multi-factor authentication (MFA), and biometrics.
Authorization
Authorization determines what users can do upon authorization. Using the concept of the least privilege principle, users only receive the access they truly need.
Example: Role-based access control (RBAC) and permission levels for enhanced security testing.
Encryption
Encryption is a core feature of application-level security. Encryption algorithms offer encryption and data protection for sensitive data, both at rest and in transit.
Example: AES, TLS/SSL, and HTTPS.
Logging
Logging is a critical feature of application-level security. This feature provides a record of activities and system events. By combining logging and monitoring, you can detect threats and strengthen API security.
Web Application Firewall (WAF)
A web application firewall (WAF) acts as a protective filter between users and web apps. It aims to block malicious requests. With configuration hardening and application security testing, WAF can enhance thorough defense.
Application Security Categories
Application security categories group apps and environments by risk. Based on the groups, businesses determine how to install protective measures. Categorization helps protect sensitive data from cyberattacks. That is how you ensure integrity and resilience.
Web Application Security
Web application security protects websites and online services from threats. Web apps run on remote servers and send data. Thus, attackers often target them to seek sensitive information or disruption.
Businesses must focus on web app security. Common threats include cross-site scripting (XSS) and SQL injection. Misconfigurations sometimes happen, too. The OWASP Top Ten has listed them all.
You should use application security testing methods like web app firewalls (WAFs) and HTTPS encryption. They work to block malicious traffic and reduce exposure. Once the data is secure, you can protect customers and maintain continuity.
API Security
Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) enable software systems to communicate and share data. So, you need API security to protect them. APIs drive microservices and the API economy. They are prime targets for attackers.
Vulnerable APIs have caused major breaches. The main reasons are weak authentication, data exposure, and poor rate limiting. The 2025 Global State of API Security Report found that 57% of organizations faced incidents related to API. What’s worse, you may suffer from data loss. Further consequences include financial damage and business disruption.
So, you must defend APIs through strong authentication. Try access controls along with API discovery and protection. API security testing helps reduce risks and safeguard sensitive data. The right API tools ensure continuity in digital ecosystems.
Cloud-Native Application Security
Cloud-native application security protects apps built with microservices, containers, and serverless platforms. Container orchestration platforms are highly dynamic. Plus, components keep spinning up and down, making it hard to control.
The State of Cloud-Native Security Report 2024 found that 71% of organizations had flaws due to rushed deployments. One of the most common cloud threats is misconfigurations. Businesses also report insecure serverless functions and vulnerable container images.
For risk management, you should apply IaC scanning and secure configurations. Automated vulnerability checks and continuous monitoring are necessary, too. Shift left security is critical as well. You should also combine cloud application security with API security. Together, they safeguard sensitive data to reduce operational risks.
Operating System (OS) Security
Even a single OS-level flaw can compromise every app and dataset it supports. Thus, operating system security is vital. Attackers often exploit this core layer and cause malware. Other threats include weak authentication, privilege escalation, and denial-of-service.
The 2024 Edgescan Vulnerability Statistics Report showed that 34.4% of infrastructure flaws were critical or high-risk. This figure included those in operational systems.
Effective defenses include strong access controls and encryption. At the same time, you should work on patches, audits, and firewalls. Businesses also need configuration scanners to detect faults early. Together, they harden the OS and reduce attack surfaces. You will have resilient, secure operation environments.
Common Application Security Risks and Vulnerabilities
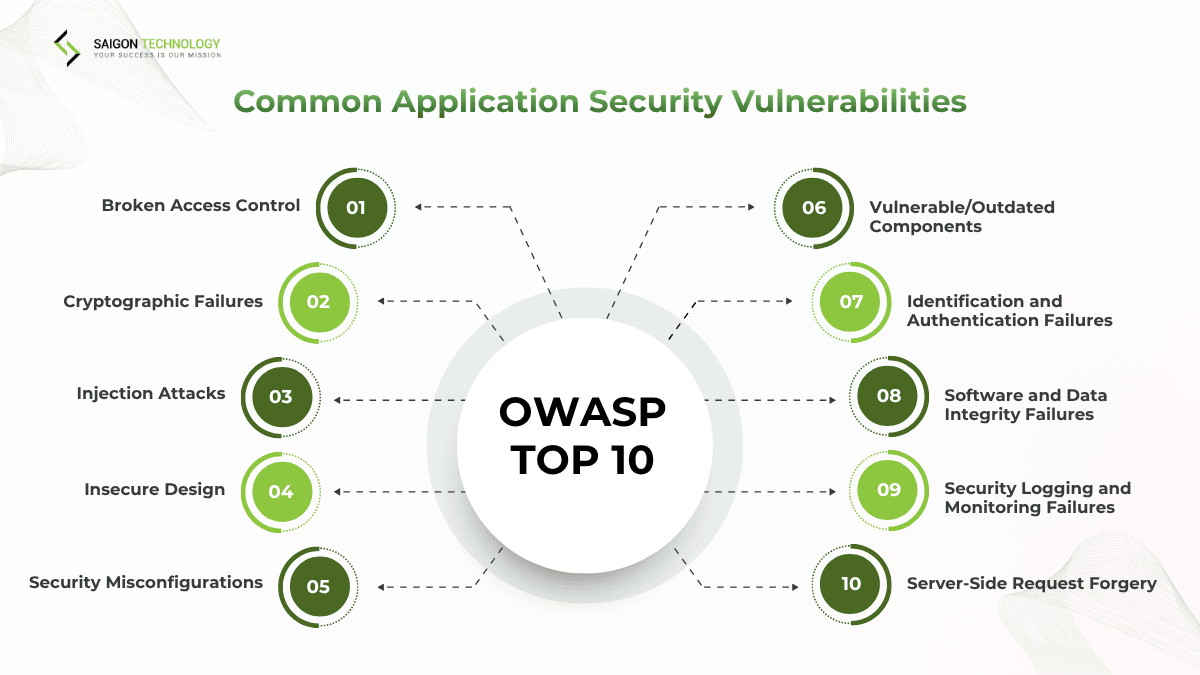
The OWASP Top 10 is a globally recognized standard. Here are the key security risks that the standard highlights that developers and organizations should watch for:
Broken Access Control
Broken access control happens when your apps fail to properly restrict user actions. Attackers may get confidential records. Then, they change another user’s data or perform admin tasks without authorization. According to the OWASP Top 10, it’s a major application security risk.
To reduce exposure, organizations should:
- Apply least privilege and validate roles.
- Use application security testing tools like DAST.
- Enforce Strict processes to protect your data and support compliance, reducing reputational damage.
Cryptographic Failures
Cryptographic failures occur when apps rely on weak encryption. Outdated algorithms and poor key management can also be the causes. You will risk sensitive data such as passwords, financial records, and personal details.
This issue ranked A02 in the OWASP Top 10 as a critical application security concern. OWASP 2021 shows rates as high as 46.44%. Organizations should adopt modern standards like AES and TLS 1.3. Plus, enforce encryption in transit and at rest to strengthen key management. Automated security testing in CI/CD pipelines helps detect misconfigurations early as well.
Injection Attacks (e.g., SQL Injection)
You encounter injection attacks when attackers insert malicious code into your app. The code can be SQL, NoSQL, or command injection. In this case, it has to execute unintended actions. OWASP 2021 reported injection flaws in 94% of tested apps. The max incidence rate was 19%. These attacks threaten both apps and API security.
To defend them, organizations should:
- Use parameterized queries and prepared statements.
- Employ strict input validation.
- Work with application security testing tools like SASR in CI/CD pipelines to fix errors before deployment.
Insecure Design
Insecure design refers to flaws in an app’s architecture or logic. The flaws expose your app to attacks, even when the code itself is correct. Ranked A04 in the OWASP Top 10, it’s one of the most serious application security risks. The issue is costly to fix later.
Organizations should follow secure design principles. Developers need to perform threat modeling to lower long-term risks. In the meantime, you can maintain customer trust.
Security Misconfigurations
Security misconfiguration happens when apps, servers, or cloud environments have insecure settings. The sources can be default passwords, open storage, or excessive permissions. This issue ranked A05 in the OWASP Top 10.
You should follow these tips to reduce long-term risks and protect customer trust:
- Apply secure design principles.
- Do threat modeling for your security testing.
- Review architecture early in the application security process.
Vulnerable/Outdated Components
Components here can be libraries, frameworks, or third-party plugins. Once they become outdated and vulnerable, they may cause breaches and downtime. Unauthorized users can then access your systems.. So, these flaws rank A06 in the OWASP Top 10.
Application security testing is essential. It would be best to track dependencies with SBOMs. You should apply patches without delay and use Software Composition Analysis (SCA) tools as well. Modern technologies ensure you can identify and remedy vulnerabilities.
Identification and Authentication Failures
This issue arises when systems don’t properly verify users. Your application will be exposed to unauthorized access. Other problems are privilege escalation and session hijacking. The OWASP Top 10:2021 ranked it 07 on the list. It also poses serious risks to API security. The main causes are:
- Weak passwords
- Insecure session handling
- Flawed login flows
To avoid it, organizations should:
- Enforce multi-factor authentication (MFA).
- Apply robust password requirements.
- Regularly test authentication processes.
Software and Data Integrity Failures
Software and data integrity fail when apps rely on untrusted updates. Other potential causes include insecure plugins or unchecked data sources. Then, attackers may inject malicious code. They can even alter critical data. Ranked A08 in the OWASP Top 10:2021, these flaws often drive supply chain attacks.
You should enforce code signing as part of the application security process. Remember to verify all updates and secure CI/CD pipelines against tampering.
Security Logging and Monitoring Failures
Security logging and monitoring failures occur when systems don’t track activities properly. You can’t then detect and respond to attacks in real time. This issue lets attackers maintain access, escalate attacks, or tamper with data unnoticed. The serious consequences make it rank A09 in the OWASP Top 10:2021.
You should install comprehensive logging. Besides, store logs securely and use automated monitoring. This way, you can flag suspicious activities early.
Server-Side Request Forgery (SSRF)
SSRF happens when attackers trick a server into making unauthorized requests to internal systems or cloud services. This issue reveals sensitive data. Attackers can scan internal networks and access cloud metadata. So, this problem ranked A10 in the OWASP Top 10:2021.
To solve it, use strong application security practices. We recommend strict URL validation, sanitization, and allowlists. Also, limit server access. Perform application security testing regularly, too, to spot issues and solve them as soon as possible.
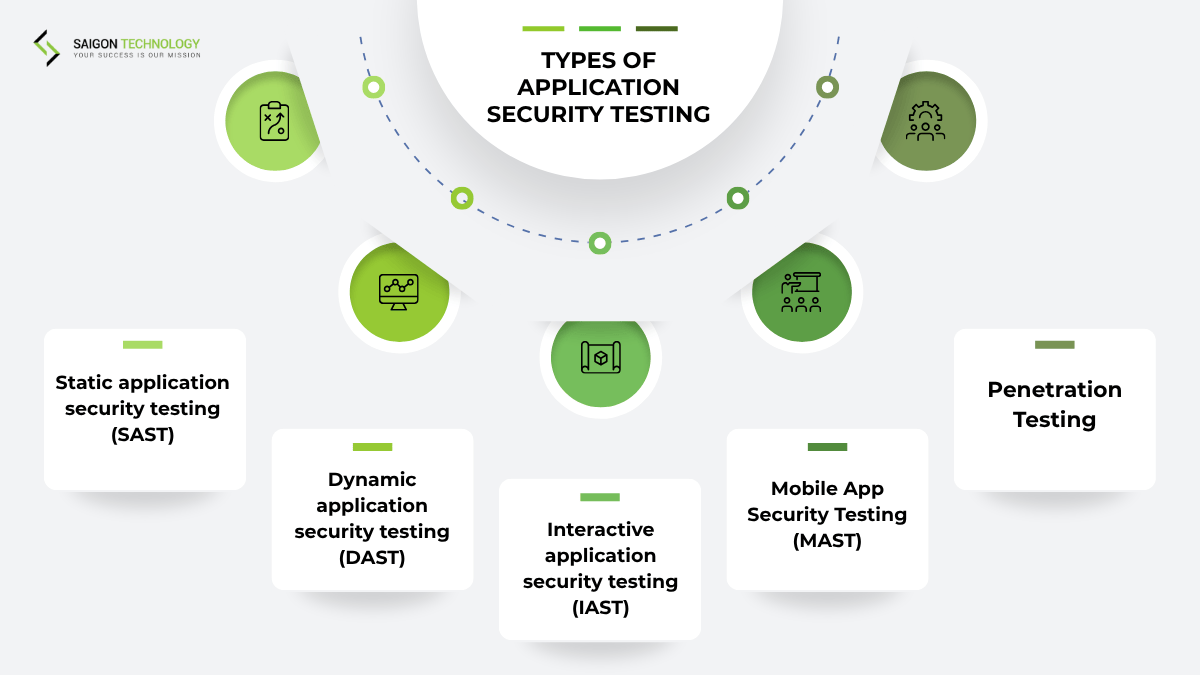
Types of Application Security Testing
Application Security Testing (AST) is about finding and fixing software issues to prevent cyber attacks. AST uses automated tools and manual methods like penetration tests and security audits.
You can scan in both authenticated and unauthenticated states. This way, you will explore flaws that attackers may exploit. Organizations should focus on public-facing systems. Integrate security testing into development, too, to prevent breaches.
AST includes SAST, DAST, IAST, MAST, and penetration testing so that it can address security from a different angle. This section explains how these approaches create a complete protection strategy.
Static application security testing (SAST)
SAST analyzes source code or binaries. The key is that it tests your app without executing the program. This test identifies coding flaws early in the lifecycle. This way, SAST helps reduce remediation costs.
You can strengthen your app from the ground up. Besides, you should integrate SAST tools into CI/CD pipelines. Then, you can automate code reviews to ensure security application development.
Dynamic application security testing (DAST)
DAST analyzes apps while they run. This concept simulates real-world attacks. Using a black-box method, it finds input validation errors, authentication flaws, and misconfiguration.
You integrate DAST into the lifecycle. Then, it detects issues in production-like environments. This application development security method also helps fix risks before attackers find them.
Interactive application security testing (IAST)
IAST combines SAST and DAST. This approach features in-app sensors to monitor behavior in real time. It provides accurate feedback and reduces false positives. Since IAST speeds up fixes, you can use it for Agile and DevOps.
As part of the application security process, it improves accuracy. Organizations can ensure faster, more secure development.
Mobile App Security Testing (MAST)
MAST identifies and fixes errors in mobile apps. It combines SAST, DAST, and penetration testing in one place. You use this package to analyze code. The test also allows you to analyze architecture and runtime behavior. Supporting modern application security technologies helps uncover issues before they impact users.
Penetration Testing
Penetration testing is a controlled simulation of cyberattacks. This adversary-based testing approach uses techniques like SQL injection, XSS, and privilege escalation. Penetration testing includes black box security testing and business logic testing.
You can also use it to check for API security. This test can be manual or automated. For better application data security, you need it for compliance in data-sensitive industries.
Application Security Tools and Solutions
You need more than just secure coding to protect your apps. Here are some tools and solutions to help you identify risks and strengthen defenses.
Application Discovery
Application discovery locates and monitors all apps and their dependencies across servers, clouds, and containers. It shows both known and hidden apps, helping reduce shadow IT and meet compliance needs. This process strengthens application security by exposing risks early.
Application Assessment
Application assessment aims to evaluate software to measure how secure it is. At the same time, you can work on performance testing and business value. Technical assessment steps include security testing and penetration tests.
You can perform compliance checks with standards like OWASP, NIST, and ISO 27001. Then, based on the checks, you decide to modernize, maintain, or retire your app. Plus, regular tests help improve security posture. Ultimately, you can reduce risks and make informed investments.
Software Composition Analysis (SCA)
SCA helps secure third-party components and open-source security within apps. It scans dependencies to find outdated or vulnerable libraries. You can receive alerts to patch the errors quickly.
SCA tools also secure license compliance to reduce legal risks. As part of the application security process, SCA strengthens data and application security.
Software Bill of Materials (SBOM)
SBOM is a software component inventory. It lists every element in an application, including open-source and proprietary modules. Thanks to its help, you can identify open-source risks and manage them faster. SBOMs assist with supply chain security and support compliance. You can use it to improve vulnerability management. By maintaining SBOM, organizations can streamline patching processes. It also reduces application security risks.
Vulnerability Management
Vulnerability management is a continuous process. Right here, you find, assess, and fix security weaknesses. The scanning tools compare systems against the CVE database to detect issues early.
You can apply patch management to close gaps immediately. These actions support risk reduction and strengthen cyber resilience. Ultimately, you can improve both API security and application security testing.
Web Application Firewall (WAF)
WAF filters HTTP/S traffic and blocks threats before they reach servers. Hence, it can protect web apps. This solution acts as a reverse proxy. Plus, it defends against application-layer attacks. You can use it to prevent SQL injection and cross-site scripting (XSS) attacks.
Runtime Application Self-Protection (RASP)
RASP works within an app’s own runtime environment security. Then, it detects and blocks threats instantly. This method uses application behavior monitoring. You aim to spot unusual actions and get real-time attack prevention.
You can stop malicious activities, issue alerts, and reduce false positives. Defense DevOps and Agile workflows become stronger then. You now have continuous protection and practical use cases.
Intrusion Prevention Systems (IPS)
IPS enhances network security by detecting and stopping threats. The system performs automated blocking and drops harmful traffic. At the same time, you remove malicious content for real-time threat prevention. It would be best to integrate it into security application development.
IPS tools complement security testing to help reduce response times. In the end, you can prevent breaches and strengthen overall network resilience.
Cloud-Native AppSec Platforms (CNAPP)
CNAPP combines CWPP, CSPM, Kubernetes security, and API security into one solution for modern cloud environments. This approach delivers comprehensive cloud-native security across the entire lifecycle. By integrating with DevSecOps workflows, CNAPP simplifies management.
Application Migration Security
Application migration security safeguards apps and data during transfers between environments. Strong access controls, encryption, and vulnerability scanning are essential before migration.
Organizations should use automated tools with cloud migration security checks. Together, they work to improve overall application development security. Ultimately, you can ensure compliance and minimize downtime.
Application Monitoring
Application monitoring means you track application performance, uptime, and security events. All happens in real-time. Modern application security technologies integrate security monitoring. Then, they detect anomalies like unauthorized access or abnormal traffic spikes. AI further assists this method. With AI-driven monitoring, you can spot risks early and strengthen API security.
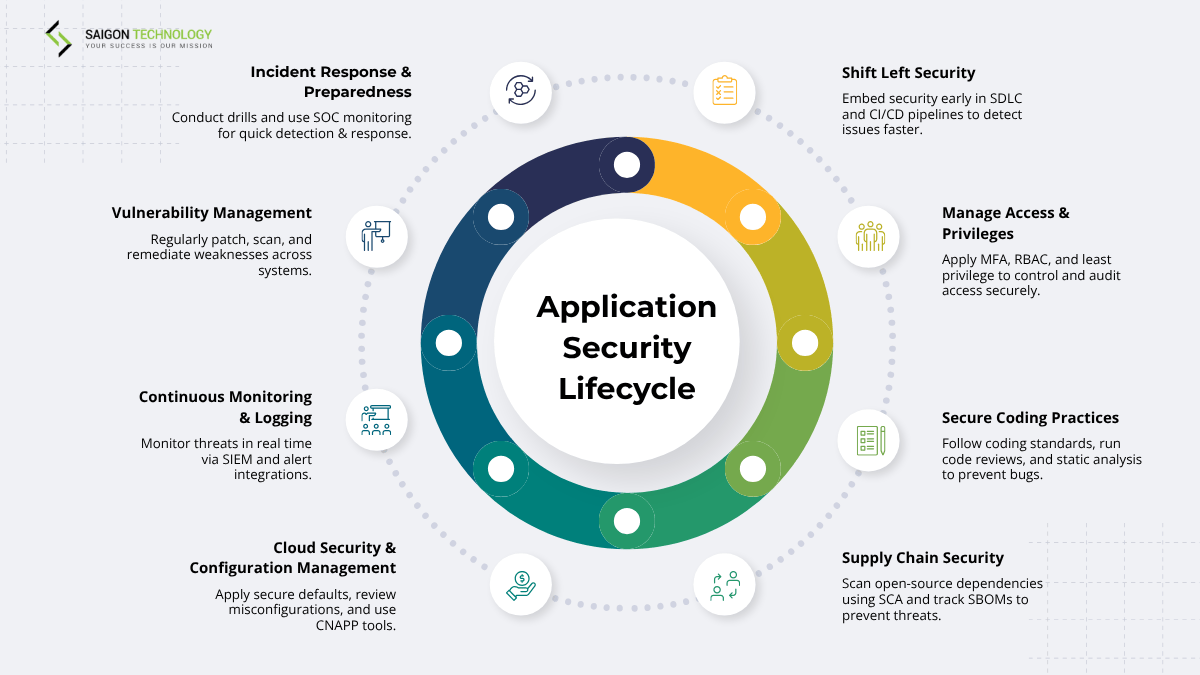
Best Practices for Application Security
Effective application security starts with a strategic plan. Below are some key practices you should follow.
Shift Left Security (DevSecOps)
Shift-left security is when you embed application security early in the secure SDLC. This way, you don’t have to wait until development is complete. You integrate application security testing into the CI/CD pipeline security. This proactive DevSecOps approach offers many benefits. For example:
- You foster collaboration between developers and security teams. Thus, every release can be faster.
- As you identify vulnerabilities soon and fix them immediately, you will enhance code quality.
- Shift-left security aims to strengthen compliance and reduce delays.
Manage Access & Privileges (MFA, RBAC)
Controlling access is a key part of the application security process. Role-based access control (RBAC) means users only get the permissions they need. You should also apply the least privilege principle.
In addition, enforce multi-factor authentication (MFA) to verify users. Plus, follow strong access control policies. These measures help you block unauthorized access. Remember to conduct regular audits, too, to ensure API security.
Secure Coding Practices
Strong, secure coding practices help prevent errors during development and improve overall application security. Developers should follow secure standards and conduct code reviews.
Static analysis tools and training programs also help developers write high-quality code. Remember to implement secret management to protect your data.
Supply Chain Security
Third-party software and open-source libraries may expose hidden threats. In this case, you can try a strong application security approach with Software Composition Analysis (SCA) and SBOMs.
You can then track dependencies and vet vendors carefully. Plus, conduct regular application security testing for new vulnerabilities.
Cloud Security & Configuration Management
Misconfigurations are one of the most frequent application security examples leading to cloud breaches. So, you should use cloud security best practices. More specifically, apply secure default settings and regularly review configurations. Besides, use Cloud-Native Application Protection Platforms (CNAPP) to automate posture management.
Continuous Monitoring & Logging
Ongoing monitoring helps you prepare properly for application security challenges. For example, you can store logs securely. Plus, remember to integrate alerts with incident response tools. Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) platforms also help centralize data.
From there, you can detect threats early. Don’t forget to combine them with application security testing to ensure a fast response.
Vulnerability Management
Establish a continuous patch management program to reduce application security risks. A strong program includes regularly scanning apps and third-party components. Plus, track findings and remediate critical issues quickly to minimize API security risks.
Incident Response & Preparedness
Strong application development security requires a clear incident response plan. So, you need to conduct drills and train staff. Besides, put detection, containment, and recovery processes in place.
A dedicated Security Operations Center (SOC) helps you monitor your app 24/7. Hence, you can ensure a rapid response once issues arise.
Measure Application Security Results
An effective application security model relies on measurable metrics. For example, you need to track time-to-remediation (MTTR). Also, keep an eye on the number of vulnerabilities resolved.
Pay attention to compliance scores and overall security posture, too. Continuous application security testing keeps security goals aligned with business objectives.
Real-World Examples and Case Studies
Real-world cases show how weak application security can lead to major losses. Learn from the examples to improve your business.
Major Breaches Caused by Poor AppSec
- Equifax (2017): This incident must be one of the most notorious major breaches. Attackers exploited open source vulnerabilities in Apache Struts (CVE-2017-5638). The patch was available but not applied. The breach exposed data of 147 million Americans. Equifax paid over $1.4 billion in settlements. It remains among the major application security challenges. You can use it as an example of an application security failure.
- Capital One (2019): A cloud misconfiguration exposed data from 100 million users. Authentication flaws and poor logging made detection slow. The company paid $80 million in fines for failing to manage the risks.
- SolarWinds (2020): Hackers added malicious code to Orion updates. About 18,000 customers were compromised. Weak business logic testing and vendor oversight led to the attack.
Lessons Learned
You need a proven application security approach to avoid potential issues. After failure, the organizations above have learned something.
- Apply patches promptly: Equifax showed how delays in patching open-source flaws can lead to serious problems.
- Secure cloud configurations: Capital One proved that cloud security is a shared responsibility. Organizations must validate configurations and enforce strict authentication controls.
- Strengthen supply chain security: SolarWinds highlighted the need to monitor third-party vendors. They applied continuous security testing and business logic testing.
- Adopt DevSecOps culture: Organizations should embed security early in the SDLC through adversary-based testing. This way, they can detect flaws before release. Other solutions include black-box testing and automated scans.
- Improve monitoring and runtime defense: Breaches often exploit logging gaps. A real-time view of security vulnerabilities can reduce the risk. Organizations should also consider runtime protection and defense for serverless containers.
Success Stories
There are many successful application security examples to check out, too, such as:
- Microsoft: Microsoft embeds application security protection into every phase of its software development lifecycle. The SDL framework emphasizes secure coding. Threat modeling and automated tools help identify issues and fix them earlier.
- Netflix (Cloud-Native Security): Netflix created and open-sourced Security Monkey. This tool monitors cloud account configurations and flags security issues. It tracked 45 AWS services, 4 GCP services, and 130 checks. Netflix also applies Chaos Engineering and DevSecOps practices. These measures improve resilience in serverless container environments.
- Google (Bug Bounty & Continuous Monitoring): Google rewards good researchers. You just need to find input validation errors, authentication flaws, or other security issues. This adversary-based testing approach works in sync with logging and monitoring. Google also offers runtime protection and layered defenses.
Conclusion
Application security (AppSec) helps protect sensitive data. You can also meet compliance needs and build customer trust. Moreover, application security testing prevents open-source risks and strengthens authentication. With continuous monitoring, users and businesses can stay safe.
Saigon Technology builds software with high application security protection. Our team follows the OWASP Top Ten frameworks. Additionally, we use modern testing tools like SAST, DAST, and SCA. This way, we ensure every app is secure and scalable. You will be ready to face cyber threats.
Is security your top concern? Then, Saigon Technology must be what you need. As a trusted app development company, we will help your business innovate with confidence. Contact us now to get started!
FAQ
1. What is the difference between application security and cybersecurity?
Cybersecurity means you safeguard all digital systems, networks, and data. Application security is a subset of cybersecurity. You protect your apps from threats and vulnerabilities. There is no unauthorized access across their entire lifecycle.
2. What are the most common application vulnerabilities?
Some application security examples are:
- SQL injection
- Cross-site scripting (XSS)
- Broken authentication
- Insecure deserialization
- Misconfigurations
3. What is the difference between application security testing and API security testing?
Application security testing evaluates the overall app security. You examine source code, configurations, and runtime behavior. Then, you can identify vulnerabilities across the system.
API security testing focuses specifically on APIs. You check the risks in API security. Besides, you deal with object-level authorization and input validation errors. This approach also handles excessive data exposure.
4. What is the difference between SAST, DAST, and SCA?
These methods work on code and runtime. The differences are:
- SAST: This method analyzes source code or binaries without execution.
- DAST: You can examine apps in a running state. This method detects flaws during runtime and supports both web and API security testing.
- SCA: You identify known vulnerabilities in third-party libraries and open source components.
5. What are the future trends in Application Security?
New trends emerge to adapt to modern cyber threats. Here are some ideas:
- AI & Automation in Security: AI-driven tools assist you in detecting vulnerabilities. They cut false positives and speed up pentesting. AI-powered tools can detect up to 95% of errors faster than traditional methods.
- Zero Trust Architecture for Applications: This application security model always checks users, apps, and services. You can try principles like “assume breach.” Also, enforce least privilege to build a stronger defense strategy for applications.
- Continuous Testing in CI/CD Pipelines: Automated testing and Zero Trust practices inside CI/CD pipelines help you find errors early. You can then lower costs.
6. How is application security integrated into the Software Development Lifecycle (SDLC)?
Application security is built into each stage of the SDLC. Developers apply secure coding practices. More specifically, they perform threat modeling and automated testing. Early integration finds vulnerabilities before release. This approach reduces both cost and risk.
7. How does Saigon Technology implement DevSecOps in the development process?
We integrate security into every phase. Our application security process has:
- Static Application Security Testing (SAST)
- Dynamic Application Security Testing (DAST)
- Software Composition Analysis (SCA)
8. What are the best tools for application security?
The best tools include:
- WAFs (Cloudflare, AWS WAF, and ModSecurity)
- SAST/DAST/SCA tools (Veracode, SonarQube, Checkmarx, and OWASP ZAP)
- Monitoring/Logging (Splunk, ELK Stack, and Datadog Security)
9. What application security services does Saigon Technology offer?
Saigon Technology offers end-to-end software development services, and all come with strong security. We offer OWASP Top 10 compliance. Our secure coding practices strengthen your apps. Automated testing tools like Selenium and Postman help us work faster while keeping quality high. We also perform regular security audits in every phase of the development process.
10. How often should I test my application security?
It depends on the test. For example:
- Automated scans: If you work on automated scans, run them weekly. You can also work on them continuously in CI/CD pipelines.
- Penetration testing: These tests are necessary quarterly. You may need them before major releases as well.
- Full security audits: Perform comprehensive tests every year. Otherwise, follow compliance requirements.
11. What certifications does Saigon Technology hold related to security?
Saigon Technology is an ISO 27001-certified company. Our experienced developers ensure strict data protection. It also supports effective risk management. We guarantee to apply privacy practices across all projects.